In the modern digital era, the term “cloud computing” is ubiquitous, and at the forefront of this revolution stands Amazon Web Services (AWS). More than just a buzzword, AWS is a powerful, comprehensive, and widely adopted cloud platform that has transformed how businesses of all sizes build, deploy, and scale their applications and infrastructure. If you’re navigating the complexities of digital transformation, understanding AWS is not just beneficial—it’s essential.
What is AWS?
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered pay-as-you-go basis. Launched in 2006, AWS essentially allows you to rent computing resources and services from Amazon’s vast global data centers, eliminating the need for businesses to purchase, own, and maintain their own physical IT infrastructure.
At its core, AWS offers an incredibly broad and deep set of services designed to provide:
Scalability: Instantly provision or de-provision resources to match fluctuating demand, from a small website to a global enterprise application.
Flexibility: Choose from a wide array of operating systems, programming languages, web application platforms, databases, and other services.
Cost-Effectiveness: Pay only for the resources you consume, converting capital expenditures (CapEx) into variable operational expenses (OpEx).
Reliability: Benefit from Amazon’s highly available, fault-tolerant infrastructure, designed for maximum uptime.
Security: Leverage AWS’s world-class security expertise and compliance certifications to protect your data and applications.
Innovation: Access cutting-edge technologies and services that are continuously evolving and expanding.
From hosting simple websites to running complex machine learning models, AWS provides the foundational building blocks for virtually any digital workload, empowering businesses to innovate faster, operate more efficiently, and reach a global audience.
Key Things You Should Know About AWS and AWS.Amazon.Com
Market Leader: AWS is the undisputed global leader in cloud computing, holding a significant market share. This dominance translates into a mature platform, extensive documentation, a massive community, and a rich ecosystem of third-party tools and partners.
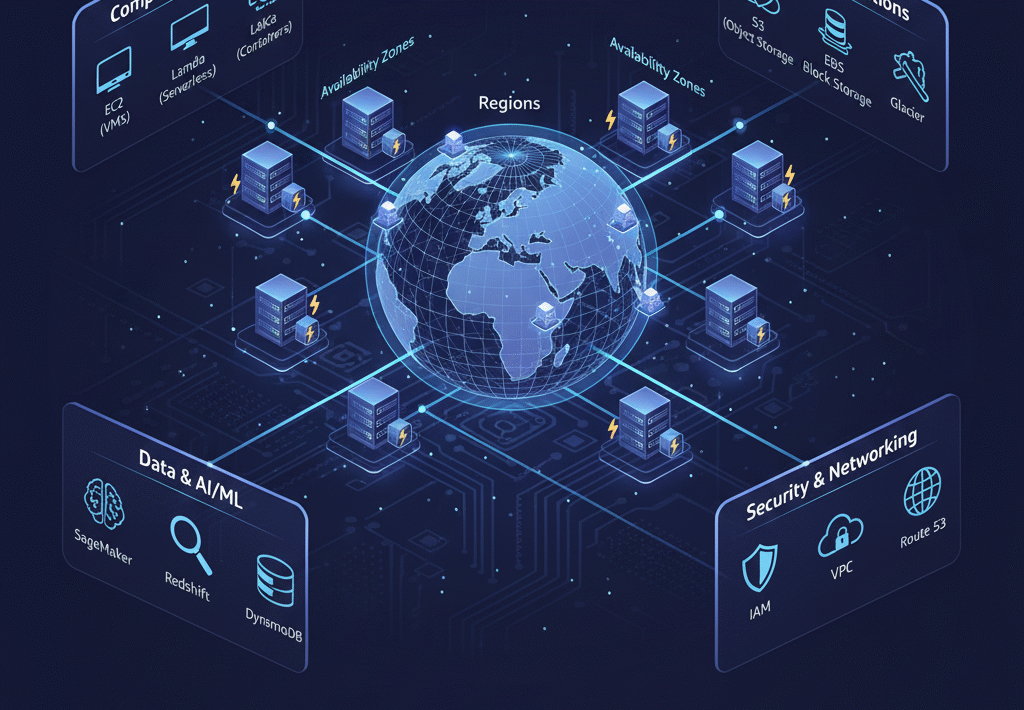
Vast Array of Services: AWS offers over 200 fully featured services, making it incredibly comprehensive. These services span categories such as:
Compute: Amazon EC2 (virtual servers), AWS Lambda (serverless functions), Amazon ECS/EKS (container orchestration).
Storage: Amazon S3 (object storage), Amazon EBS (block storage), Amazon Glacier (archive storage).
Databases: Amazon RDS (managed relational databases), Amazon DynamoDB (NoSQL), Amazon Aurora (high-performance relational).
Networking: Amazon VPC (virtual private cloud), Route 53 (DNS), Elastic Load Balancing.
Machine Learning: Amazon SageMaker, Rekognition, Comprehend.
Analytics: Amazon Redshift (data warehousing), Amazon Kinesis, AWS Glue.
Security, Management & Governance: AWS IAM, CloudWatch, CloudTrail.
Global Infrastructure: AWS boasts an extensive global infrastructure, comprised of Regions and Availability Zones. A Region is a physical location in the world where AWS clusters data centers. An Availability Zone (AZ) consists of one or more discrete data centers, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity, housed in separate facilities. This design provides high availability and fault tolerance.
Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: One of the most attractive aspects of AWS is its flexible pricing model. You typically pay only for the compute power, storage, and other resources you actually use, with no long-term contracts or upfront commitments. This allows for significant cost savings and agility.
Robust Security Model: AWS operates under a “shared responsibility model” for security. AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud (protecting the infrastructure), while customers are responsible for security in the cloud (securing their applications, data, configurations, etc.). AWS provides a vast array of security tools and services (like IAM for access control, VPC for network isolation) to help customers fulfill their responsibilities.
Serverless Computing with Lambda: AWS pioneered serverless computing with AWS Lambda. This service allows developers to run code without provisioning or managing servers, automatically scaling and charging only for the compute time consumed. It’s ideal for event-driven applications, microservices, and rapid development.
Strong Developer Tools and Ecosystem: AWS offers a comprehensive set of developer tools, including SDKs for various programming languages, command-line interfaces (CLIs), and integration with popular IDEs. The vast community ensures abundant tutorials, forums, and third-party integrations.
Enterprise-Grade Capabilities: AWS is trusted by some of the world’s largest enterprises and governments for mission-critical workloads. Its extensive feature set, security, and compliance certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC, HIPAA, GDPR) make it suitable for highly regulated industries.
AWS.Amazon.Com as Your Gateway: The official AWS website (aws.amazon.com) is the central hub for:
Product Information: Detailed descriptions and documentation for every service.
Pricing Details: In-depth information on cost structures for each service.
Learning Resources: Tutorials, whitepapers, training courses, and certification paths.
Case Studies: Real-world examples of how businesses leverage AWS.
AWS Management Console: The web-based interface for managing your AWS resources.
Free Tier: Information on services you can use for free, up to certain limits, to get started.
Why AWS is Indispensable for Modern Businesses
For companies looking to thrive in the digital age, AWS provides a crucial foundation:
Agility and Speed to Market: Quickly provision resources and deploy applications, accelerating innovation and reducing time to market for new products and services.
Reduced Costs: Eliminate the need for expensive hardware purchases and maintenance, paying only for what you use.
Global Reach: Easily deploy applications and data closer to your customers worldwide, improving performance and user experience.
Focus on Innovation: Offload infrastructure management to AWS, allowing your teams to concentrate on developing core business solutions.
Scalability for Growth: Seamlessly scale your infrastructure to meet unpredictable demand, supporting rapid business growth without costly over-provisioning.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Leverage AWS’s robust security features and compliance certifications to protect your data and meet regulatory requirements.
FAQs about AWS
Q1: Is AWS only for large companies?
A1: No, absolutely not. While large enterprises heavily use AWS, its pay-as-you-go model and extensive range of services make it incredibly accessible and cost-effective for startups, small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), and even individual developers.Q2: What is the AWS Free Tier?
A2: The AWS Free Tier allows new AWS customers to get hands-on experience with many AWS services at no charge, up to certain usage limits. It includes services that are always free, 12 months free, and short-term trials, making it perfect for learning and experimentation.Q3: What are the most commonly used AWS services?
A3: Some of the most frequently used services include Amazon EC2 (virtual servers), Amazon S3 (object storage), Amazon RDS (managed databases), AWS Lambda (serverless compute), and Amazon VPC (virtual networking).Q4: How does AWS pricing work?
A4: AWS uses a pay-as-you-go model. You’re charged based on your actual consumption of resources (e.g., compute time, storage volume, data transfer). Pricing varies by service and often includes tiers for different usage levels, as well as options like Reserved Instances for cost savings on predictable workloads.Q5: Is AWS secure? Who is responsible for security?
A5: AWS is very secure, implementing robust physical, operational, and software security measures for its infrastructure. AWS follows a “shared responsibility model.” AWS is responsible for the security of the cloud (the underlying infrastructure), while customers are responsible for security in the cloud (their data, applications, configurations, and network settings within their AWS account).Q6: What is a “Region” and “Availability Zone” in AWS?
A6: An AWS Region is a geographical area that hosts multiple isolated locations. An Availability Zone (AZ) is one or more discrete data centers within a Region, each with independent power, networking, and connectivity. Using multiple AZs within a Region helps ensure high availability and fault tolerance for applications.Conclusion
Amazon Web Services stands as a titan in the cloud computing industry, offering an unparalleled breadth and depth of services that empower businesses to innovate, scale, and transform their operations. Its global infrastructure, flexible pricing, robust security, and continuous innovation make it an indispensable platform for companies navigating the complexities of the digital age. By thoroughly exploring aws.amazon.com and leveraging its vast resources, individuals and organizations can unlock the immense potential of cloud computing and build the future on AWS.
Views: 624